Hand Tracking in VR/AR using RF Frequency Signals
Authors: Elvis Dsouza, Dr Shelly Vishwakarma (UoS), Dr Kevin Chetty (UCL)
Abstract
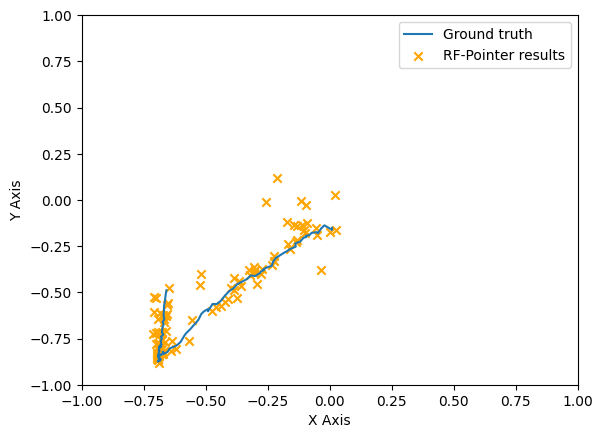
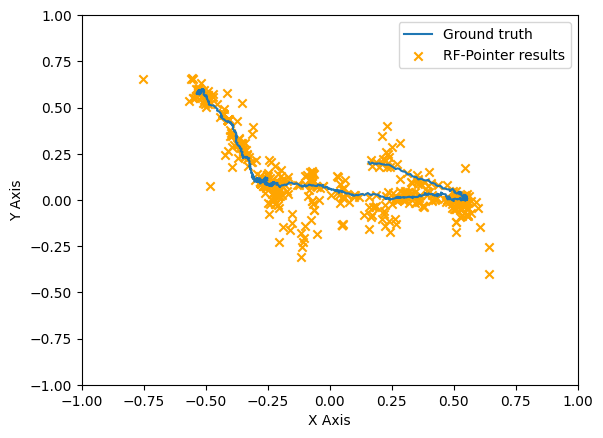
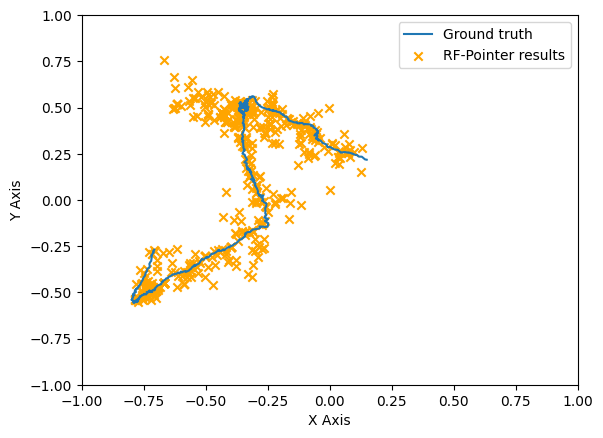
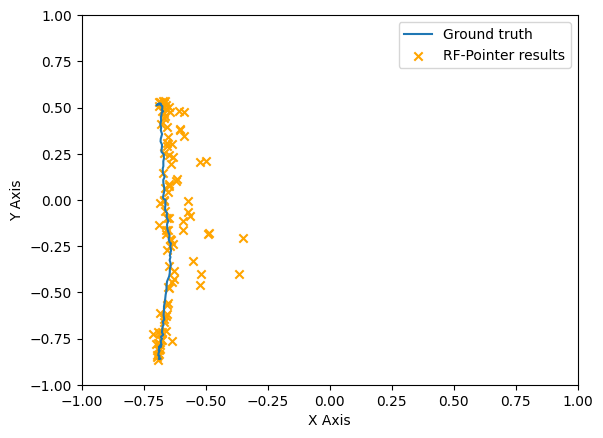
This research and development work introduces the "RF-Pointer", an innovative radio-frequency-based interaction framework designed for real-time tracking and projection of hand movements in virtual spaces. The system can provide a hands-free and distinctive interaction experience suitable for virtual reality and augmented reality. In this study, we delve into the architectural and operational dynamics of the RF-Pointer, utilizing a prototype equipped with a 77 GHz radar sensor. Initial tests reveal an average tracking error of less than 3 cm in estimating the pointer’s location. To further illustrate the efficacy of the proposed architecture, we conduct a qualitative comparison, presenting the results in the form of tracked trajectories corresponding to both ground truth and the RF-Pointer estimated trajectories. The tracking results demonstrate that RF-Pointer trajectories closely align with ground truth trajectories.
Setup
The chosen setup after many prototypes was with AWR1642 77 GHz Radar sensor. This is ideal for a preliminary study as the data received is a manageable size and easy to process. The size of the data determines the real-time performance as converting raw radar data to a 3D point cloud can be a performance bottleneck.
Results
The results were assessed both qualitatively and with accuracy for natural hand motions and gestures. A few example visualisations for tracking predictions over ground truth is shown in the figures above. A more detailed analysis will be published in the paper.